Contents
Communication Media (Transmission Media)
The communication medium also called transmission medium is the physical path through which a message travels from sender to receiver. The communication media acts as a communication channel for linking various computing devices so that they may interact with each other. The most commonly used communication media include cable, satellite, microwaves, fiber optics, etc.
Computers and telecommunication devices use signals to represent data. These signals are transmitted from a device to another in the form of electromagnetic energy. Communication devices are the tools used by senders and receivers to deliver and receive messages. More specifically, “Communication devices route and transmit information to various devices, including radio and telephone systems. Common examples of communication devices are telephones, cellular phones, wireless mobile devices, GPS (Global Positioning System) technology systems, radios, and transmitters, etc.
Types of Communication Media
Basically, there are two types of communication media. They are:
- Wired Communication Media/ Guided Media
- Wireless Communication Media/ Unguided Media
a. Wired or Guided Communication Media
This type of communication media in which different types of wires such as twisted-pair cable, coaxial cable, fiber-optic cable, etc. are used to transfer data among computers. It is also known as guided or bounded transmission media in which data are transmitted within a closed path using interconnected wires or cables. It refers to all types of physical wire through which data travels from one location to another. The following are the subtype of wired communication media.
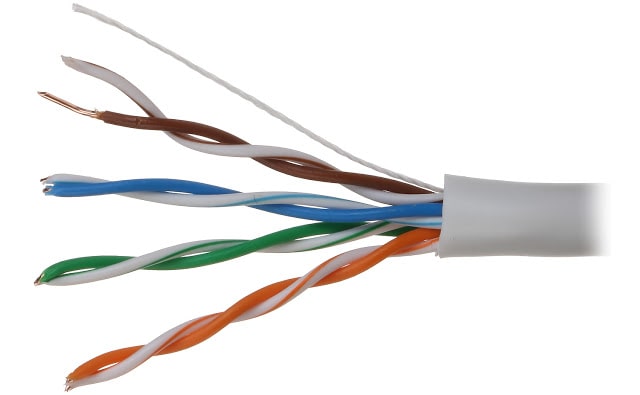
i. Twisted-pair cable
The twisted-pair cable is the most commonly used transmission media. This type of wire is widely used in telephone lines. So, it is often called telephone wire. It consists of copper wires twisted into pairs with each wire insulated with plastic. Twisted pair cables are of two types:
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP)
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP)
Cables with a shield are called Shielded Twisted Pair and commonly abbreviated STP. Cables without a shield are called Unshielded Twisted Pair or UTP. Twisting the wires together results in a characteristic impedance (resistance) for the cable. Some characteristics of Twisted Pair cable are low cost, easy to install, high-speed capacity, high attenuation, 100-meter limit, etc. Its main drawback is short distance due to attenuation.
ii. Coaxial Cable
A coaxial cable is an electrical cable with an inner conductor surrounded by an insulating layer, surrounded by conducting shield. Coaxial Cable consists of two conductors i.e. inner conductor and outer conductor. The inner conductor is held inside an insulator with the other conductor woven around it proving a shield. An insulating protective coating called a jacket covers the outer conductor. The outer shield protects the inner conductor from outside electrical signals. Coaxial cable is used as a transmission line for radio frequency signals, in applications such as connecting radio transmitters and receivers with their antennas, computer network connecting, and distributing cable television signals. Coaxial cables are mostly used in long distances because it is usually free from external disturbances.
Some characteristics of coaxial cable are low cost, easy to install, medium of attenuation, up to 100 Mbps capacity, etc. The main drawback of this cable is single cable failure can take down an entire network.
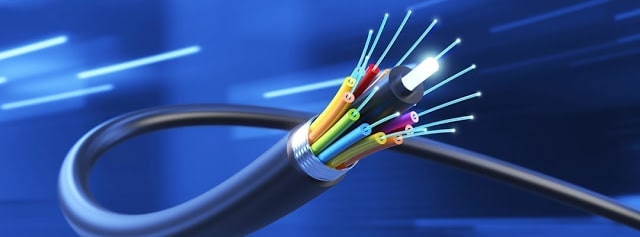
iii. Fiber-Optic Cable
The fiber optic is a technology that uses glass or plastic threads (fibers) to transmit data. It consists of a bundle of glass threads, each of which is capable of transmitting messages modulated onto light waves. In this cable, a thin filament of glass fiber is wrapped in a productive jacket and multiple fibers are placed in the same cable. Data are transferred in the form of light along with the optic fiber at the speed of light. In this cable, the data transmission rate is billions of bits per second. This cable is more powerful than co-axial cable and twisted pair cable. This cable is not affected by electromagnetic radiation. In this cable, the data error is very less than other cables. It is the most widely used cable today. The main weakness of fiber optics cable is that it is fragile and difficult to install.
b. Wireless or Unguided Communication Media
Wireless technology is rapidly increasing the latest type of communication technology today. Due to its flexibility, it is being more popular. It uses radio signals or infrared signals for transmitting and receiving data. It is also known as unguided or unbounded transmission media because the signals are not bounded to a particular direction as a wired system. The commonly used wireless communication system are discussed below.
i. Microwave System
In the microwave system, high-frequency radio signals are used to transfer data through space. These signals can travel only on the straightway and they cannot bend. The hills and mountains can block the signals. The transmitter and receiver of a microwave system should be in a line of sight so, they are mounted on very high towers.
ii. Radio Wave System
Radio waves can be used for many different uses in a quick and effective way. As most radio waves are caused naturally, it ensures that radio waves are the reliable sources to use, since radio waves have been around since the Earth. People may not realize it, but radio waves are in fact used in everyday life without hesitation.
Sound consists of pressure variations in the matter, such as air or water. Sound will not travel through a vacuum. Radio waves, like visible light, infrared, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays, are electromagnetic waves that travel through a vacuum. When you turn on the radio you hear sounds because the transmitter at the radio station has converted the sound waves into electromagnetic waves, which are then encoded onto an electromagnetic wave in the radio frequency range (generally in the range of 500-1600 kHz for AM stations, or 86-107 MHz for FM stations).
Radio electromagnetic waves are used because they can travel very large distances through the atmosphere without being greatly attenuated (long and narrow) due to scattering or absorption (the ability of a substance to observe energy). Your radio receives the radio waves, decodes this information, and uses a speaker to change it back into a sound wave.
iii. Communication Satellite
A communication satellite is an artificial satellite placed in outer space for the purpose of telecommunications. Modern communication satellites use a variety of orbits including geostationary orbits, Molniya orbits, other elliptical orbits, and low Earth orbits. It works as a microwave relay station. It is placed in outer space and moves its own orbit like other satellites. The satellite is visible from any point of the earth so the sender and receiver can easily communicate with each other by using an antenna aiming at the satellite. Placing the satellite along the earth’s orbit takes a very high cost.
iv. Bluetooth Technology
Bluetooth technology is a wireless technology that connects electronic devices while they are close to each other. Bluetooth creates a Personal-Area Network (PAN) just for you. Cell phones can be paired with wireless Bluetooth headsets. Bluetooth technology is also compatible with personal computers, laptops, printers, GPS (Global Positioning System) receivers, digital cameras, telephones, video games, etc.
v. Infrared Transmission
Infrared (IR) is a wireless transmission medium that sends signals using infrared light waves. Infrared signals have frequencies between 300 GHz to 400 THz. IR waves are used for short-range communication (no more than 5 meters). IR cannot pass through solid objects, like walls. This helps to prevent interference between one system and another. In this system, one room cannot be affected by the infrared waves in another room. It is cheap, easy to build, and does not require any government license to use. IR waves offer higher bandwidth for use. A good example of an infrared signal is the remote control used in TV, AC, etc. It is also used in devices such as the mouse, wireless keyboard, and printers.
vi. Laser Transmission
This type of transmission uses a thin laser to transfer data up to few kilometers. Laser beams are unidirectional, therefore this type of transmission system use line of sight propagation. In such a transmission system, a photodetector and the laser are set on both the sender and receiver sides. Such a system offers a very high band at a very low cost. The major problem in this transmission system is that laser beams cannot go through rain or thick fog.
vii. Wi-Fi Technology (Wireless-Fidelity)
Wi-Fi is a popular wireless technology that uses radio waves to provide wireless high-speed network connections. Wi-Fi uses both single-carrier direct-sequence spread spectrum radio technology and multi-carrier Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (OFDM) radio technology. Wi-Fi is supported by many applications and devices such as Laptops, notebooks, mobile phones, etc. The major operating system supports Wi-Fi. It creates Personal-Area Network (PAN) and a Home network. Bluetooth and Wi-Fi are different in several ways. Wi-Fi technology boasts faster data transfer speeds and range, making it a good replacement for Ethernet Systems.
Difference between Guided Media and Unguided Communication Media
| Guided Media | Unguided Media |
| This is a type of communication media that uses physical cable or wire for data transmission. | This is a type of communication media in which data are transmitted through the air. |
| It is mainly suited for point-to-point-line configuration systems. | It is mainly used for broadcasting purposes. |
| The signal transmits in the form of voltage, current, or light in guided media. | The signal transmits in the form of electromagnetic waves in unguided media. |
| Examples: Twisted Pair Cable, Co-axial Cable, Optical Fiber Cable, etc. | Examples: Microwave Radio Links, Infrared, etc. |